

CSTAR
London Health Sciences Centre University Hospital
339 Windermere Road
London, ON
N6A 5A5
Phone: 519-663-3111
or 519-685-8500 ext. 33111
Fax: 519-663-8401
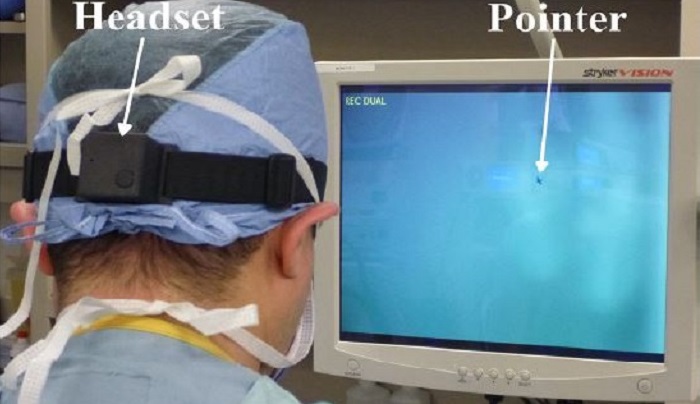
A CSTAR study where the participating instructor surgeon wears a headband which projects a mouse pointer onto the surgical monitors in the OR. The purpose of wearing the headband is for a teaching tool.
Laparoscopic surgery is a type of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) in which long slender instruments and a laparoscope enters the patient’s body through small incisions. Although MIS reduces tissue trauma, post-operative pain and recovery time, it requires a high level of experience and skill, and poses challenges to surgical trainees. Conventionally, a significant part of a junior surgeon’s training takes place in the operating room where they are tasked with either assisting in the operation or performing the procedure by themselves under the direct supervision of a senior surgeon. This form of training requires good collaboration between the instructor surgeon and operating surgeon. During the operation, the instructor surgeon and operating surgeon typically have both hands occupied by surgical instruments and each have their own operating monitor on which the surgical image appears. Currently, there are no formal methods of instruction or teaching in the OR apart from conventional verbal instruction. The WHaSP (Wireless Hands-Free Surgical Pointer) is a headband that the instructor surgeon wears to project a mouse pointer onto the surgical monitor. This pointer is used as a teaching tool during laparoscopic surgery.
The overall objective of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of the WHaSP system under real operating conditions. The specific objective is to evaluate the efficiency of using the WHaSP as compared with conventional methods while providing instruction during minimally invasive surgery by measuring instruction times during procedures. The hypothesis is that the use of the WHaSP increases the efficiency and ease of instruction during minimally invasive surgery, as measured by a reduction in task completion time of at least 15% when using the pointer system.